Preparation of Alkanes in Laboratory
Alkanes are hydrocarbons only has carbon and hydrogen atoms in it's molecules. There are only single bonds between carbon atoms in alkane molecules. Alkanes are prepared from other organic chemicals such as alkenes, alkynes, alkyl halides, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids using suitable reagents under specific conditions.
Content - Reactions to prepare alkanes
- Preparation of Alkanes by unsaturated Hydrocarbon
- Catalytic hydrogenation of alkenes
- Catalytic hydrogenation of alkynes
- Preparation of Alkanes by alkyl halides
- Grignard reagent and water reaction to prepare alkane
- Grignard reagent and alkyl halide reaction
- Wurtz reaction
- Preparation of Alkanes by Carbonyl compounds
- Preparation of Alkanes by aldehydes
- Preparation of Alkanes by Ketones
- Preparation of Alkanes by Carboxylic acids
Preparation of Alkanes by unsaturated Hydrocarbon
Alkenes and Alkynes are considered as unsaturated hydrocarbons in organic chemistry. Alkene and alkyne compounds can be converted into alkane compounds by catalytic hydrogenation with supply of proper temperature. Raney Nickle(Ni), Platinum(Pt), or Palladium(Pd) are used as catalysts under higher temperature for the hydrogenation process.
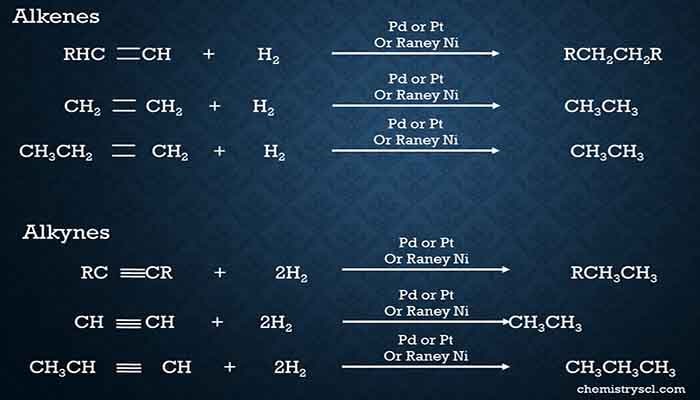
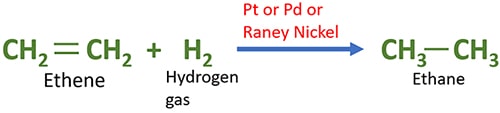
Catalytic hydrogenation of alkenes
In hydrogenation of alkenes, two hydrogen atoms are attached to two carbon atoms which have made a double bond in the alkene.
Catalytic hydrogenation of Ethene with hydrogen gas
Ethane is given as the result of addition of two hydrogen atoms to ethene.
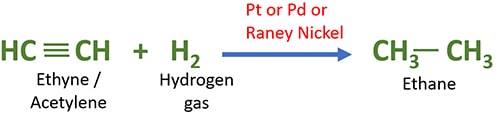
Catalytic hydrogenation of alkynes
In alkynes, there is a triple bond between two carbon atoms. There is the possibility of adding four hydrogen atoms to such alkyne compound in hydrogenation of alkyne.
Catalytic hydrogenation of acetylene (ethyne) with hydrogen gas
Ethane is given as the result of addition of two hydrogen atoms to ethene.

Preparation of Alkanes by alkyl halides
Alkanes can be prepared by Alkyl halide as mentioned below.
- Grignard reagent and water reaction
- Grignard reagent and alkyl halide reaction
- Wurtz reaction
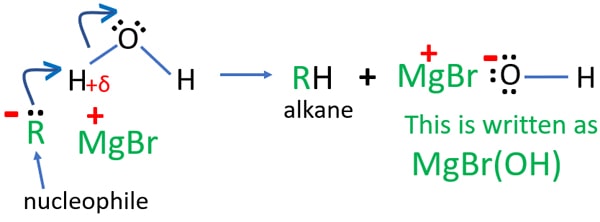
Grignard reagent and water reaction
Because Grignard reagent is not stable to water, Grignard reagent gives alkanes when Grignard reagent reacts with water or dilute acids. In this reaction, an alkane with similar number of carbon atoms included in the Grignard reagent is given.
Grignard reagent and alkyl halide reaction
This reaction gives an alkane compound which has number of carbon atoms to the summation to number of carbon atoms in alkyl halide and number of carbon atoms in Grignard reagent. Therefore, this reaction is a carbon-chain extension reaction.
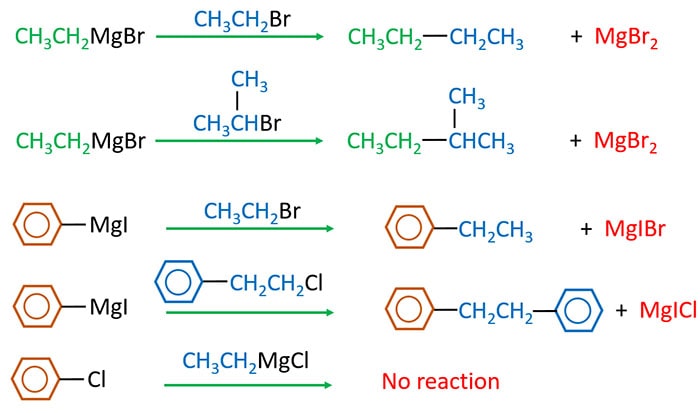
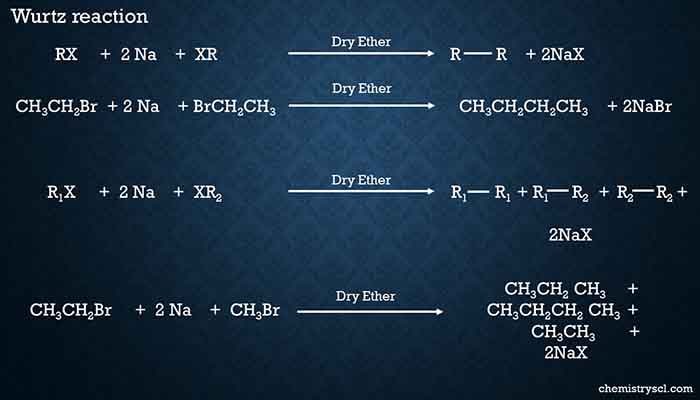
Wurtz reactions to prepare Alkane
Alkyl halides are treated with sodium in dry ether. Then a symmetrical alkanes containing twice the number of carbon atoms of alkyl halide is obtained
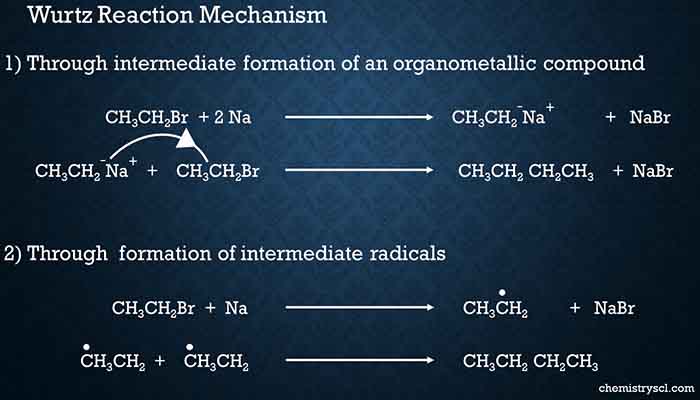
Mechanisms of Wurtz reaction
There are 2 suggested mechanisms for Wurtz Reaction
- Through intermediate formation of an organometallic compound
- Through formation of intermediate radicals
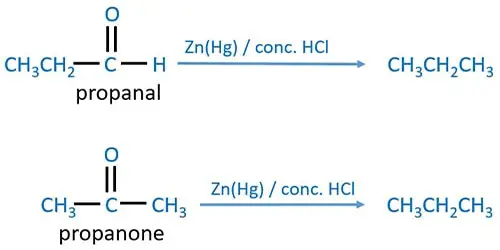
Preparation of Alkanes by Carbonyl compounds
Carbonyl group of carbonyl compounds (aldehyde or ketone) is reduced by clemmensen reduction. Zn(Hg) and concentrated HCl is used as the Clemmensen reagent. Carbonyl carbon group is reduced to an alkyl group (-CH2) in this reaction.
Preparation of Alkanes by Carboxylic acids
Every carboxylic acids (aliphatic and aromatic carboxylic acids) are subjected to decarboxylation. Hydrocarbons are given as products. A mixture of solid Calcium (CaO) or Calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) with Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is used as the reagent in decarboxylation process.

Questions