Physical Properties, IUPAC Nomenclature and Isomers of Alkene
Alkene is a hydrocarbon compound and there is at least one double bonds between two carbon atoms. Alkenes are introduced as olefin. Due to existence of double bonds, alkene are considered as unsaturated hydrocarbons and physical and chemical properties are heavily affected due to that. But, in this tutorial, we only focus physical properties of alkene and chemical properties of alkenes are discussed in a separate tutorial.
Content
- Physical properties of alkenes
- IUPAC Nomenclature of alkenes
- Isomers of alkenes
- Steps of drawing isomers
- How physical properties vary with each isomer
Physical properties of alkenes
Under physical properties, we will see physical status at room temperature, meting and boiling points of alkene.
Physical states of alkenes at room temperature
Physical state of the alkene compound at room temperature depend on the strength of intermolecular forces and molecular mass of respective alkene as other compounds.
- Ethene, Propene, n-butene which are simplest alkene compounds are gases.
- Alkenes containing carbon atoms 5 to 18 are liquids.
- More than 18 carbon atoms in alkenes are solids.
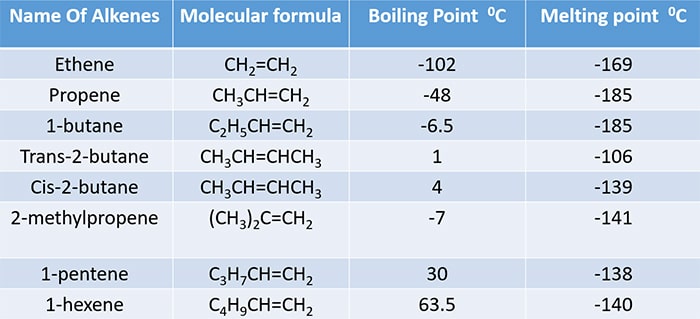
Melting and Boiling points of alkenes
Alkenes have higher melting and boiling points than the corresponding alkanes because alkenes have a pi ( Π ) bond in it's double bond. Pi ( Π ) bonds are more polarizable than sigma (σ) bonds. Therefore intermolecular forces between alkene molecules are more stronger than between alkane molecules.
As other compound series, boiling and melting points are increased with molecular mass.
IUPAC Nomenclature of alkenes
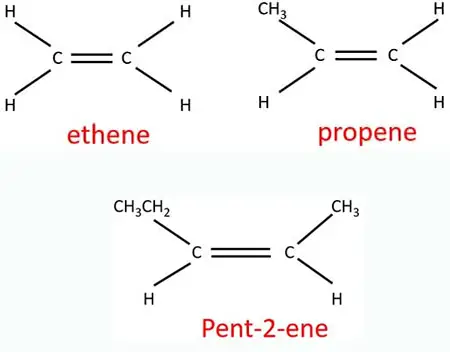
We can give a IUPAC name to every alkene compound. Usually IUPAC nomenclature of an alkene compound ends with "ene" suffix such as "ethene, "propene and etc. Because alkene compounds are simple in structure, it is not difficult to naming alkenes.
How to name when there are two or more double bonds in an alkene compound
There may be two or more double bonds in some alkene compounds.

Isomerism of alkenes
Geometrical isomerism is the important isomerism case we study in alkenes due to double bond of alkenes. Other isomerism cases such as optical, chain and position isomerism cases also may be exist.
General formula of alkenes
CnH2n [n=2,3,4....]
Ex: if n=3;
Respective hydrocarbon : C3H2*3 = C3H6
What is the simplest alkene
Simplest alkene contains only two carbon atoms. According to the general formula of alkene, number of hydrogen atoms are four in the simplest alkene. Therefore ethene( C2H4 ) is the simplest alkene.
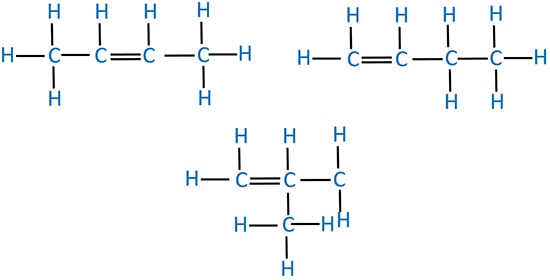
Structural isomers of alkenes
Chain and position isomers are demonstrated by alkenes as structural isomers.
Structural isomers of butene
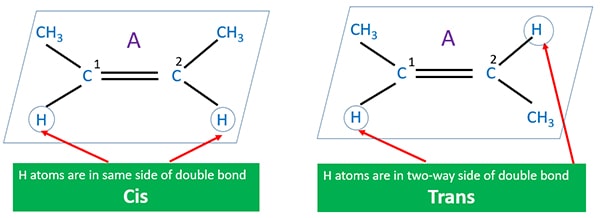
Geometrical isomerism of 2-butene
There are two geometrical isomerism in 2-butene.
Geometrical isomerism of C5H10
Geometrical isomerism structures for are figured below.
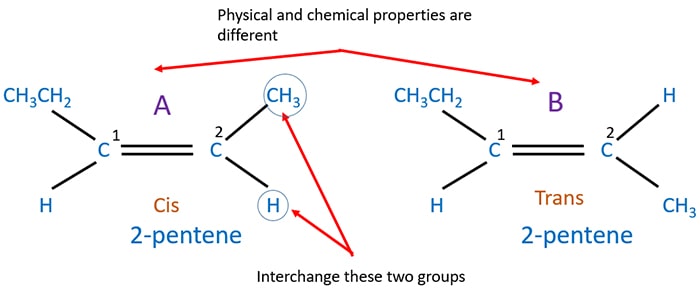
Study the figure. You can see the number 2 carbon in the molecule A has two different groups as -CH3 and -H. If we interchange that two groups we get a new compound. Physical and chemical properties of A and B are different. A structure is cis isomerism and B is trans isomerism.
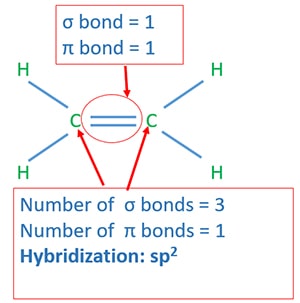
Hybridization of alkenes
Hybridization of ethene
Ethene only has two carbon atoms which are bonded by a double bond. Each carbon atom has three hydrogen atoms. When consider one carbon atom, it has three σ bonds and one Π bond. Therefore hybridization of that carbon ato is sp3.
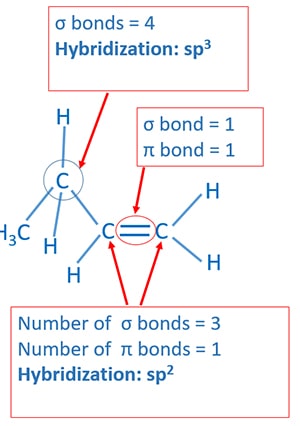
Hybridization of propene
Sources of alkenes
Many industrial important alkenes are taken from breaking petroleum. Petroleum is heated upto very high temperature. Then molecules of petroleum are gone under thermolysis. These alkenes are converted into other important compounds.
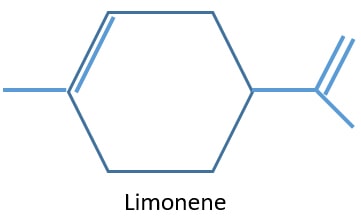
Natural sources of alkenes
There are alkenes in aromatic oils in plants. Limonene includes in lemon and orange aromatic oils. Polyisoprene is an alkene included in rubber. There is α - pinene in turpentine.
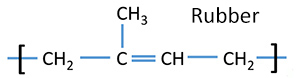
Industrial and domestic uses of alkenes
Polyethylene, ethylene dioxide, ethylene oxide, vinyl chloride are produced by ethene. Polymerization
of these compounds, very important industrial artificial polymers are produced. Ethanol, acetaldehyde
and acetic acid are produced by ethene.
Polypropylene, acrylonitrile, propylene oxide and cumene are prepared by propene.
Producing polymers using alkenes
A lot of alkenes are used to prepare polymers. These polymers are very useful in our domestic purposes.
Have Questions?