Carbonyl compounds - Aldehydes and Ketones Examples
Carbon-oxygen double bond is the active group of carbonyl compounds. There are two kinds of carbonyl compounds as aldehydes and ketones. Reactions of carbonyl group depends on nature and polarity of double bond.
Aldehyde general structure
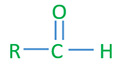
R - alkyl or aryl groups
Ketone general structure
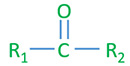
R1, R2 - alkyl or aryl groups
Aldehydes and ketones examples

Aldehyde and ketone reactions
Aldol condensation of aldehydes and ketoness
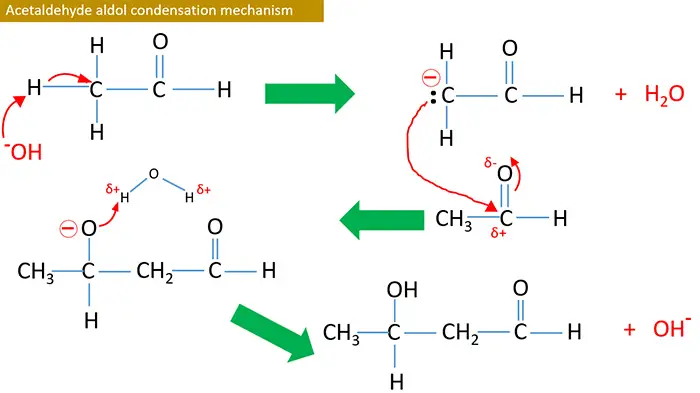
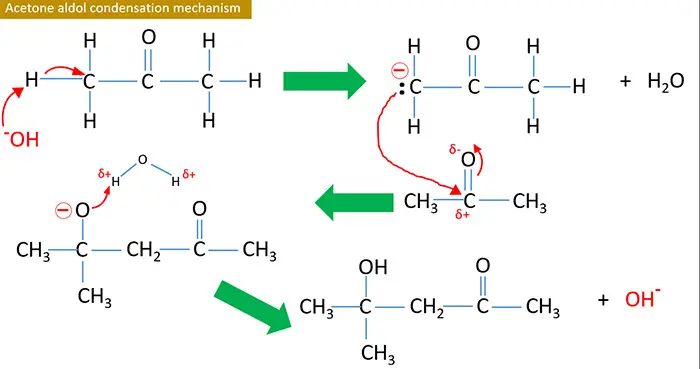
Aldol condensation is occurred only in carbonyl compounds which have a α hydrogen. These α H is acidic, therefore they are removed easily with bases and give carbanion.
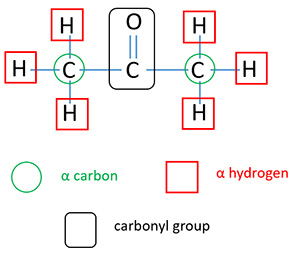
What is alfa hydrogen?
All H atoms existing on α carbon are defined as α H. All carbon atoms which are adjacent to carbonyl carbon are defined as α carbon.
Aldehyde or ketone which have αH react with any strong bases such as NaOH, KOH and Ba(OH)2 and give aldol as the product. This reaction doubles the number of carbon atoms of initial aldehyde or ketone. To dehydrate the aldol compound, it is heated alone or with I2.
Ethanal and Acetone aldol condensation
- There are two carbon atoms in ethanal molecule. But in the product, there are four carbon atoms in the carbon chain.
- Acetone (propanone) contains three carbon atoms. After reaction with NaOH(aq) or KOH(aq), there are six carbon atoms in the carbon chain.
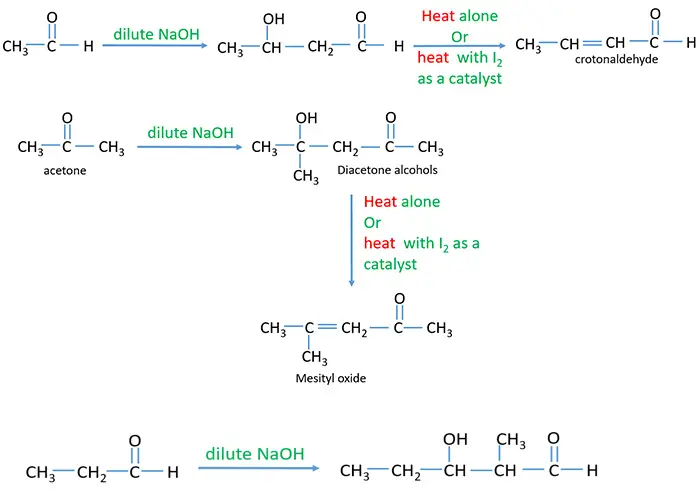
Dilute NaOH or KOH
Reaction is stared by OH- ions provided from NaOH or KOH. At the end, OH- is regenerated.
Therefore OH- ions are behaved as a catalyst.
Acetaldehyde aldol condensation mechanism
Acetone aldol condensation mechanism
Related Topics of Carbonyl Compounds | Aldehydes and Ketones