Phenol Preparing, Reactions, Physical Properties
Phenol is an oxygen substituted organic compound. Phenol is an insoluble organic compound in water. Phenol has a characteristic smell and can act as a germicidal. Preparing phenol, reactions of phenol, characteristics of phenol are sections you have to learn under phenol lesson in organic chemistry.
Figure 01: phenol molecule
Physical properties of phenol
- colourless, crystalline solid.
- Phenol turns into pink colour when it is exposed to the air.
- Melting point: 430C
- Boiling point : 1820C
- There is the characteristic carbolic acid smell
Phenol in water - Solubility of phenol in water
Phenol makes hydrogen bonds with water. Therefore phenol should be dissolved in water. Adding more phenol into the water will make separate layers of both substances.
Phenol dissolve in ether and ethanol very well.
Uses of phenol
- Dilute solutions of phenol is used as germicides.
- As a raw material of dyes, pharmaceutical, detol, bakelight.
- to manufacture herbicide
Preparation of phenol
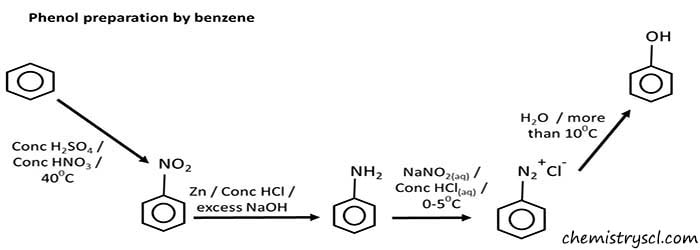
Prepare phenol from benzene
We cannot synthesis phenol from benzene in a single step. We have to follow several steps to prepare phenol from benzene.
- Benzene is translated into the nitrobenzene by adding concentrated sulfuric acid and Concentrated nitric acid at 400C.
- Aniline is prepared by reduction of nitrobenzene. Zinc, concentrated HCl as added to the nitrobenzene and then add excess NaOH to the given aniline salt to release aniline.
- Nitrous acid ( NaNO2(aq) and concentrated HCl(aq) ) is added into the aniline between 0-50C. It will produce benzene diazonium chloride.
- Finally, water is added to the benzene diazonium chloride at higher temperatures than 100C.
- Also we can add directly NaNO2(aq) and concentrated HCl(aq) to the aniline room temperature. This will also give phenol as the product.
See why nitrous acid is prepared by aqueous NaNO2 and concentrated HCl and how to prepare HNO2 acid
Reactions of phenol
Phenol is ortho para activator and a weak acid. Electrons density of benzene ring in phenol is much higher than benzene. Therefore substitutions reactions of phenol occurs much easier than benzene. Phenol reactions and their characteristics of those reaction are explained below in detail. these reactions are useful, when you want to identify phenol from other organic compounds such as aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids. Those cases are highlighted in this tutorial.
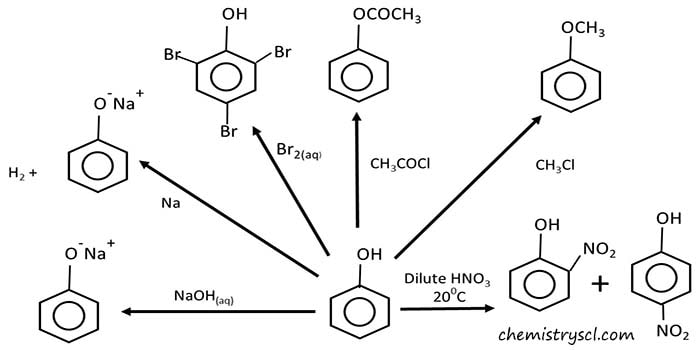
- Phenol and strong metals reaction - with sodium, potassium
- with strong alkalis like NaOH, KOH
- Phenol and halogen
- Phenol with dilute and concentrated nitric acid
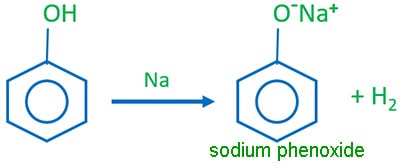
Phenol and strong metals reaction
Phenol reacts strong metals such as sodium, potassium to give hydrogen gas and sodium phenoxide. This indicates, phenol has acidic characteristics.
Phenol and aqueous NaOH reaction
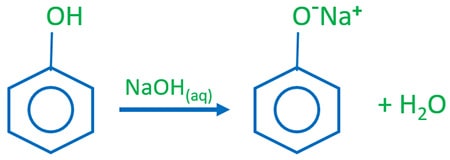
Phenol is a weaker acid than carbonic acid. Phenol reacts with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and give sodium phenoxide as the salt and water is also formed because this is an acid base reaction. This reaction can be used identify phenol from aliphatic alcohols because aliphatic alcohols do not react with aqueous NaOH. When this reaction occurs, temperature of the reaction mixture increases because this reaction is an exothermic reaction.
Phenol reacts with aqueous NaOH to give H2O and sodium phenoxide.
Phenol reacts with aqueous KOH to give H2O and potassium phenoxide.
Note: Phenol do not react with Na2CO3 or NaHCO3.
Phenol and halogen reaction
Phenol reacts with halogens easily and give precipitates. Also we don't need to add lewis acids such AlCl3.
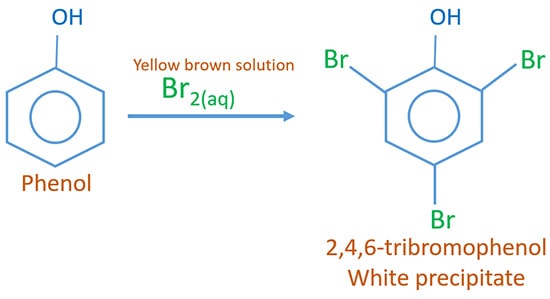
Phenol and aqueous bromine reaction
2,4,6-tribromophenol is given as the product. Aqueous Br2 solution is yellow brown in colour. When phenol is added to the Br2(aq) solution, the white precipitate, 2,4,6-tribromophenol is formed.
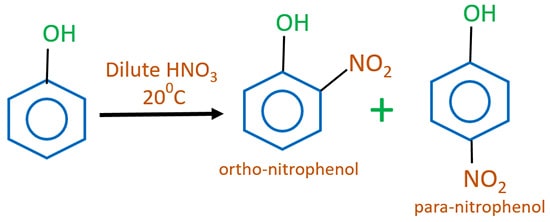
Phenol and dilute nitric acid reaction
Phenol and dilute nitric acid react to give a mixture of ortho-nitrophenol and para-nitrophenol. This shows phenol is a strong activator because we do not need concentrated HNO3 or heating.
Phenol and sodium carbonate reaction
Phenol does not react with sodium carbonate (Na2CO3). This is used to identify phenol and carboxylic acid because carboxylic acid reacts with sodium carbonate and emit carbon dioxide gas. So we can see, phenol is less acidic than carboxylic acid.
Phenol and sodium bicarbonate reaction
Phenol does not react with sodium carbonate (NaHCO3). This reaction is used to identify phenol and carboxylic acid because carboxylic acid reacts with sodium bicarbonate and emit carbon dioxide gas. From this reaction too, we can see, phenol is less acidic organic compound than carboxylic acid.
Phenol and ferric chloride
Phenol gives violet colour with ferric chloride(FeCl3). This reaction is characteristic of all compounds containing the group -C(OH)=C. This reaction can be used to identify phenol from other compounds.
Phenol with acid chloride or acid anhydride reaction
Phenyl esters are given as products.
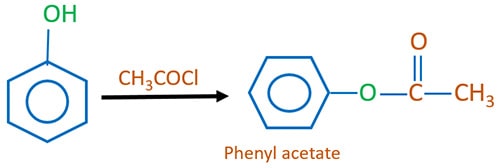
Phenol and acid chloride reaction
Phenol reacts with ethanoyl chloride to give phenyl ethanoate / phenyl acetate. Ethanoyl chloride is a acid chloride compound. In this reaction, a HCl molecule is eliminated.
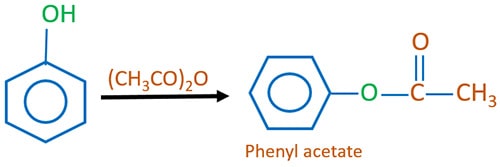
Phenol and acid anhydride
Phenyl ester is given as the product while a carboxylic acid is also produced. To recover two products, chemical separation methods has to be used like distillation.
Phenol reactions summary
Questions
give any two reaction that can be used to prepare phenol
- Aniline is treated with HNO2 at room temperature to produce phenol.
- When water is added to benzene diazonium salt, phenol is produced.
sodium phenoxide to phenol
Sodium phenoxide has weak basic characteristics. So it reacts with dilute acids to give phenol again. Add dilute HCl to sodium phenoxide to take phenol. A two layers should be separated because phenol does not dissolve in water phase.