Identify Aldehyde and Ketone - Oxidation of aldehyde
Aldehyde and ketones sometimes show similar reactions while sometimes show different reactions. However, both aldehyde and ketone contain following group. In this tutorial, we will lean how to separate (identify) aldehyde and ketone compounds.
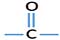
Active group of aldehyde is figured below.
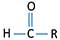
Ketone's active group is also given below.
Differences of aldehyde and ketone
Aldehyde and ketone both have similar and difference chemical properties. Aldehyde can be oxidized to carboxylic acid easily while ketone are not.
How to identify a ketone?
You can identify a ketone from acidic potassium permanganate. Purple colour of acidic potassium permanganate is not changed because there is no reaction between ketone and acidic potassium permanganate.
How to identify an aldehyde?
You can identify the aldehyde from acidic potassium permanganate. Purple colour of acidic potassium permanganate is changed to colourless because aldehyde is oxidized by acidic potassium permanganate.
Due to different active groups, aldehyde and ketone indicate different reactions for same reagent. But sometimes they show same changes (like colour changes) to some reagents.
The best way to identify aldehyde from ketone is checking the oxidizing of aldehyde or ketone compound. Observe the colour change which is related to the aldehyde compound. The colour change is occurred in aldehyde sample.
Oxidation of aldehyde
Aldehyde are oxidized to carboxylic acids by both strong and mild oxidizing agents.
Strong oxidizing agents
Aldehyde are oxidized to alcohols by strong oxidizing agents and their colour changes will notify strong oxidizing agents are being reduced.
- H+ / KMnO4: purple colour is changed to light pink or colourless.
- H+ / K2CrO4: yellow colour is changed to green
- H+ / K2Cr2O7: orange colour is changed to green
Mild strong oxidizing agents
- Tollen's Reagent
- Fehlingh's reagent
Aldehyde and tollen's reagent
Tollen's reagent is prepared by dissolving silver hydroxide, the white precipitate in ammonia solution.
When aldehyde is oxidized to carboxylic acid, Ag+ ion is reduced to Ag which is deposited in the bottom of the test tube. Deposited silver is shown as a silver mirror.
But we cannot identify formic acid from aldehyde from tollen's reagent because formic acid is oxidized to carbon dioxide. So both aldehyde and formic acid reacts with tollen's reagent and we cannot observe a different thing in two cases.
How do you identify aldehyde from formic acid?
Formic acid is the simplest carboxylic acid compound. We can use different characteristics of carboxylic acids and aldehydes to identify aldehyde from formic acid.
- Add sodium and observe changes. In one compound, a gas is emitted. Formic acid reacts with sodium and emits hydrogen gas that can be used to identify aldehyde from formic acid. Also ketones can be identified from this method.
Reduction of aldehydes and ketones to alcohols by LiAlH4 and Lucas' test
From this method, we try to produce primary and secondary alcohols and then check their differences to identify aldehyde and ketone.
- Aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols by LiAlH4
- Ketones are reduced to secondary alcohols by LiAlH4
Lucas' reagent test to identify primary alcohols and secondary alcohols
As lucas' reagent, we use anhydrous zinc chloride and concentrated hydrochloride acid (ZnCl2/HCl). This reagent is much suitable for, identify primary alcohols and secondary alcohols.
But, from good observation, you can identify primary alcohols and secondary alcohols too.
Identify primary alcohols and secondary alcohols from Lucas' reagent
- Add Lucas' reagent to two alcohol products given from aldehyde and ketone.
- Wait about 10 minutes. One solution become turbid or cloudy. That cloudy appearance is given by secondary alcohol. No visible reaction is occurred in other solution. So we can identify primary and secondary alcohols.
- So primary aldehyde is given by aldehyde. Now aldehyde and ketone are also identified.
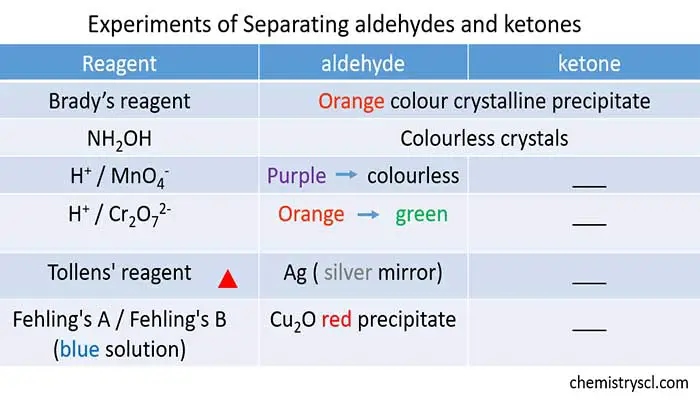
Below table shows some experiments can be done to identify aldehyde and ketone
Experiments to identify aldehyde and ketones
| Reagent | Aldehyde | Ketone |
|---|---|---|
| Brady's Reagent | Orange colour precipitate | Orange colour precipitate |
| NH2OH | Colourless precipitate, does not dissolve in water | Colourless precipitate, does not dissolve in water |
| Acidic KMnO4 | Purple colour is changed to light pink or colourless | No difference |
| Acidic K2Cr2O7 | Orange colour is changed to green | No difference |
| Tollen's Reagent | Silver deposits, (silver mirror) | No reaction |
| Fehlinghs's Reagent (blue colour) | Aliphatic aldehydes are oxidized. A brick red colour, Cu2O forms. | No reaction |
Questions
the reagent with which both aldehydes & ketones can react easily
There are so many compounds which can react with aldehyde and ketone.
Reactions common for aldehyde and ketone
Questions for you
Decide whether following statements are true or false?
Aldehydes are the product of oxidation of primary alcohol and ketone are secondary alcohols?
Correct. Oxidation of primary alcohols and secondary alcohols give aldehydes and ketones respectively.
aldehydes ketones and carboxylic acids reactions are same.
False. Aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acid have different chemical properties. But also have similar chemical properties such as reducing to alcohols from LiAlH4.
Secondary alcohol to aldehyde can be done in single step?
False. You cannot do this in single step. Then how it is possible? have to follow several reactions or sometimes it is completely impossible to do.