Oxidation Number of Carbon and Chlorine Atoms in Chloroform (CHCl3)
Chloroform, is an alkyl halide compound in organic chemistry and contains one carbon atom, three chlorine atoms and one hydrogen atoms and one hydrogen atom. In this tutorial, we are going to learn how to determine oxidation numbers of carbon and chlorine atoms in CHCl3 molecule.
Methods of finding oxidation numbers in CHCl3 molecule
There are two methods to determine oxidation numbers of atoms in molecules or ions.
- Using lewis structure of CHCl3 molecule
- Using algebraic equation of summation of individual oxidation numbers of atoms
Find oxidation numbers of atoms of CHCl3 molecule using the lewis structure
Because there are three different elements in the CHCl3 molecule, you should draw the Lewis structure carefully. However though there are three different elements, lewis structure of CHCl3 molecule can be drawn readily and the drawn lewis structure is shown below.
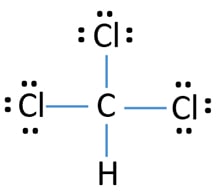
Mark direction of electrons attracting of bonds due to electronegativity difference of atoms
Atoms which have higher electronegativity values, can attract electrons of bonds towards them. Now, we will see how this will affect to the CHCl3 molecule.
Electronegativity values of carbon, chlorine and hydrogen atoms - Pauling Scale
- Carbon: 2.55
- Chlorine: 3.16
- Hydrogen: 2.2
Now, we can look how electrons are attracted between carbon, chlorine and hydrogen atoms.
- Among carbon, chlorine and hydrogen atoms Chlorine is the most electronegative element. Due to higher electronegativity, electrons of C-Cl bonds are attracted towards chlorine atoms as following image.
- Because carbon is more electronegative than hydrogen, electrons of C-H bonds are attracted towards carbon atom.
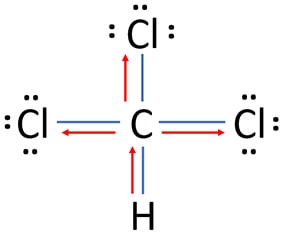
Oxidation number of chlorine atoms in CHCl3
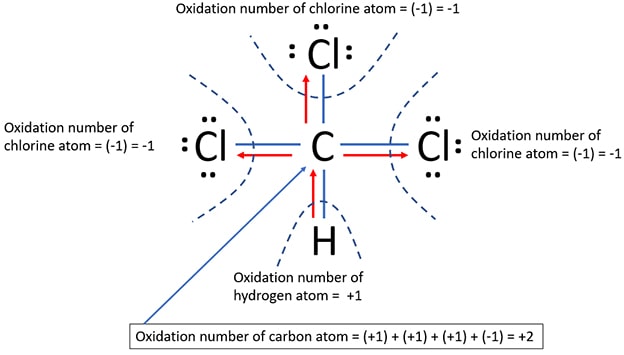
- Oxidation number of chlorine atom: According to the lewis structure of CHCl3, electrons of the C-Cl bond tend to attract towards the chlorine atom. Therefore, carbon partially loses its one electron in C-Cl bond and chlorine atom partially receives one more excess electron.
- As well, there are no charges on any chlorine atom.
- Therefore, oxidation number of each chlorine atom is -1.
Oxidation number of carbon atom in CHCl33
Because there are four bonds around carbon atom, oxidation number of carbon atom should be calculated by taking the algebraic summation of individual oxidation numbers.
- Due to carbon atom's partial lost of three electrons in three C-Cl bonds, carbon receives a +3 oxidation state.
- Because carbon partially receives an excess electron in C-H bond, carbon receives a -1 oxidation state.
- As well, there is no charge on carbon atom.
- Oxidation number of carbon atom = +1 + (+1) + (+1) + (-1) = +2
Find oxidation numbers of atoms of CHCl3 using algebraic equation
This method use an mathematical algebraic equation to find the oxidation number of an atom in molecules or ions. In this method, you can find the unknown oxidation number of an atom by using known oxidation numbers of other atoms in the molecule or ion.
This method is not 100% accurate for all molecules and ions, but can be used in lot of applications and we will try it now.
Oxidation numbers of chlorine
Chlorine has several oxidation numbers such as -1, 0, +1, +3, +5, +7. Because, chlorine is the most electronegative element, oxidation number of chlorine should be a negative one and only negative oxidation number is -1. We substitute -1 in our following algebraic equation.
Oxidation number of hydrogen
Because hydrogen has the lowest electronegativity value in CHCl3<, hydrogen's oxidation number should be a positive one hydrogen's only positive oxidation number is +1.
Summation of individual oxidation numbers of each atom = overall charge of molecule or ion
For CHCl33 molecule, overall charge is zero and we can write following algebraic equation.
Oxidation number of carbon atom + oxidation number of chlorine atoms + oxygen number of hydrogen atom = overall charge of CHCl3 molecule
Because oxidation number of carbon atom is taken as unknown, take it as x.
Apply known values for the equation.
- x*1 + (-1)*3 + (+1)*1 = 0
- x = +2
We have found that, oxidation number of carbon atom in CHCl3 molecule is +2.
Questions
What is the oxidation state of carbon in CHCl3
Oxidation number of carbon atom in CHCl3 is +2.