Industrial Steel Manufacturing Process and Production
Steel is an alloy produced by subjecting excavated materials to various process. What are the raw materials, how to get them, how behavior steel making process in history? What is the process of making steel? That lot of like problem are in front of us during discussing that topic. Now let;s solve them one by one.
Written by: Chamidhu Lakpriya, (undergraduate), Manufacturing Engineering, University of Peradeniya, Sri Lanka
In this tutorial, we will cover following of steel.
- What is steel?
- What are the raw materials of steel?
- What is the manufacturing process of steel?
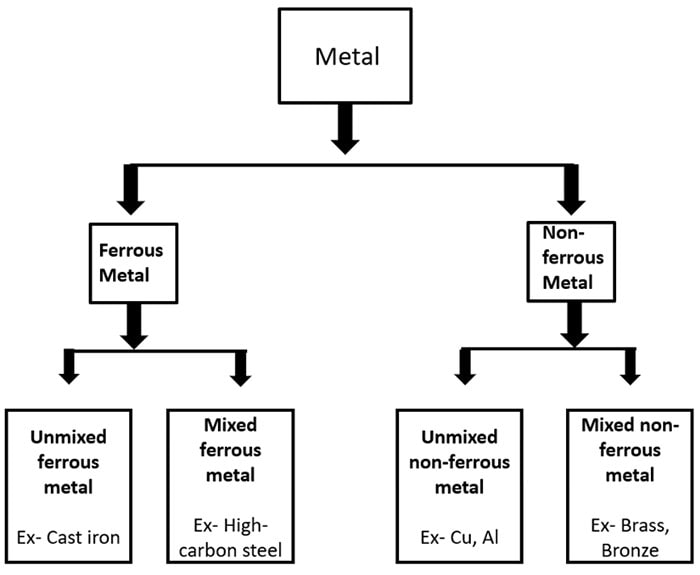
What is steel?
Steel is an alloy with low amount of carbon (carbon content must be between 0.02 and 1.5) and a little amount of other impurities. There are so many different of steel types are making by manufactures to face the different types of requirements. These types are categories as carbon steel, stainless steel, tool steel and alloy steel.
The properties of steel are the main reason to increase the demand of steel around the world. Hardness, tensile strength, yield strength, toughness, elongation, fatigue strength, plasticity corrosion and malleability are some of them.
Raw materials of steel production
In the early days of the steel industry began, the main feature of the countries where the steel industry flourished and developed was the readiness of the raw materials.
Annual worldwide steel production is going with producing steel from iron ore or scrap steel. The raw materials are varying with the method of the making steel.
Producing steel using blast furnaces is the major method of making steel. The raw materials used in that method are iron ore, coke and limestone. Steel scrap is also used as raw material in electric arc furnace process.
Iron ore
The main material contains in iron ore is Fe (Ferrous). Ferrous is not found on earth as a pure metal. It chemically bond with oxygen, silicon, Sulphur and several other materials. Combination of that materials we called as iron ore. There are two types of iron which depend on the composition of ferrous bonding with oxygen. They are magnetite (black ore - FeO.Fe2O3) or hematite (bloodstone ore - Fe2O3).
Earth's most important iron ore deposits as sedimentary rocks. Iron ore is abundant in America, Australia, Brazil, India etc. They are mined using explosives to break up or using machines to excavate. After that pieces of ore are collected and crushed by mechanics. Then, they are separated from non-metals that process called as ore-dressing. In the next step, the refined ore is mixed with coke and limestone, grind and heated to produce iron-rich feedstocks. That final output we called as sinter. Sinter is put into blast furnace to further process to making steel.
Coke
Charcoal was used to make steel around 1920 and is now replaced entirely by coal.
The reason of the adding charcoal or coke to the process is
to convert Fe into steel. Coal is mined by coal reserves situated in United states, Russia, Australia, China and etc. There are two method of
coal mining. They are surface mining and deep mining. After mining they move to another process for remove rocks, dirt, ash, sulfur and other
unwanted materials. Then coal is put into coke oven to heat coal up to 1,8000F around 18 hours. The resulting coke is put into
blast furnace to further process to making steel.
Limestone
The limestone is primarily composed of calcite (CaCO3) or calcium carbonate. They are most commonly found in shallow, calm and warm marine water. Main countries of have limestone are china, US, Russia, japan and etc. The calcite obtained from the excavation is first sent to text for the relevant calcium carbonate level. Then calcite is put in to the oven called as limekiln and heated up to about 10000C to produce limestone.
Steel scrap (ferrous scrap)
Steel is also made by recycling the waste steel (steel scrap) that is discarded on a daily basis. The main method of producing steel using scrap steel is the electric arc furnace (EAF) method.
Using steel scrap is more valuable to protect environment. That is caused to decrease CO22 emission and resource consumption is also low.
Manufacturing process of steel
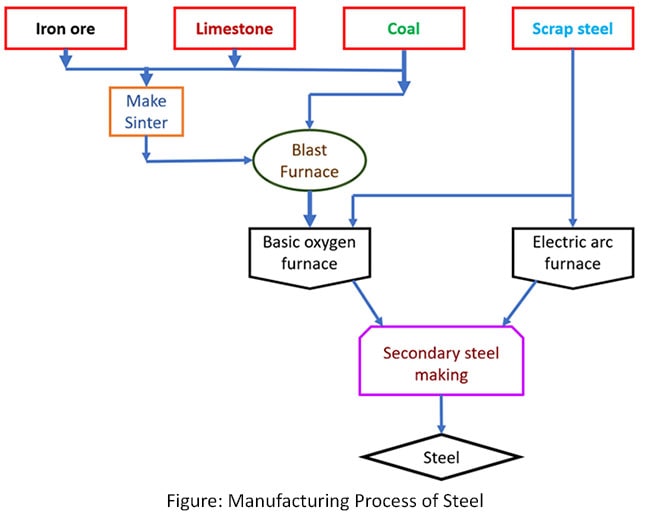
The process of manufacturing steel is taking place with two ways. The are manufacturing process and recycling process. Manufacturing process has main three steps. But, the recycling process has only two steps. There are some similarities between the two methods in terms of process.
First the main method(manufacturing) is going in three steps. There are blast furnace process, refine process and secondary steel making process.
Blast furnace process
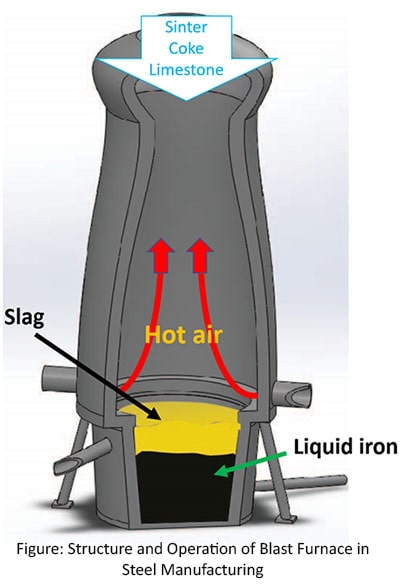
- In that step the blast furnace is used to heat the raw materials to form a basic ferrous liquid with a slag.
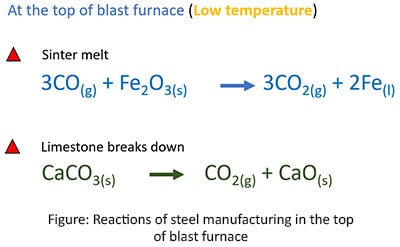
- First sinter, coke and lime are added in to the blast furnace from the upper opening. At the same time the hot air blast is injected through nozzles called as Tuyeres in the bottom of the furnace. This blast rises the temperature (up to about 22000C) in the furnace to form the reactions to make Fe liquid.
- The sinter and iron ore are melted to form a pool of iron at the bottom of the blast furnace.
- Limestone combined with impurities to form a liquid called slag that flows on a liquid iron.
- At the end of the process, liquid iron is extracted from the bottom of the furnace. Slag is skimmed off and used in other industries such as cement manufacturing.
- The hot metal we get from the blast furnace isn't pure iron. it contains impurities such as Sulphur, Phosphorus, Silicon and high percentage of Carbon that can brittle the metal. To make steel these elements must be removed or reduce.
Reactions in the bottom of the blast furnace
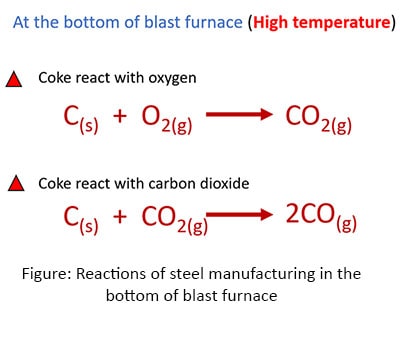
Reactions in the top of the blast furnace
Basic oxygen steelmaking (BOS)
Basic oxygen steelmaking is main bulk manufacturing process for refining iron and convert in to steel.
High carbon concentration of an iron is increased brittleness of the iron. With brittle property it is unsuitable for rolling or forging. BOC process converts iron into steel by reducing the amount of carbon in it and removing impurities.
First, steel scrap is put into the vessel. Then molten metal is added. After high purity oxygen is blown on to hot metal at about twice the speed of sound by the lance. That oxidation produces heat. The temperature is controlled around 22000C by the scrap steel and iron ore which is added also control the heat.
Carbon reacting with oxygen is produced carbon monoxide (CO(g)). Then other impurities are combined with lime and deposited as slag. Slag doing a special task by removing impurities and isolating molten metal from the air. After liquid steel is removed from the vessel to further process.
Secondary steel making
In this process liquid steel is want to be solidify and shaping or forming in to a required profile. There are three main ways to doing this. They are Sand casting, Continuous casting and Ingot casting. The temperature of the liquid steel is controlled and gases such as oxygen are removed through the addition of silicon and aluminum at the beginning of the process.
Sand casting
First the shape of the part that required is made up with mold using sand. Sand mixed with water and suitable binders are added to make a special mixture to create the mold.
Silicon is Added to increase the fluidity of the liquid. Then the liquid steel is filled in to the mold and leave to solidify.
Continuous casting
Continuous casting uses feedstock from the basic oxygen steelmaking (BOS) process. The liquid steel coming from the vessel is stored in a unit called tundish. Tundish is aided to the removal of impurities.
The liquid steel in tundish comes out through a nozzle in to a number of copper molds. The cooling is controlled and solidify is began with the outer surface of the steel shell. The molds are oscillated to protect the solidifying shell does not to break. The sickness is also reduced by adding flux. The steel shell is grown and drawn down through a curve arrangement support rolls. As the shell begins to solidify, the curve path ends and travels alone a horizontal path. After shells are cut to obtain a required length. The final output we can get as billets, blooms and slabs.
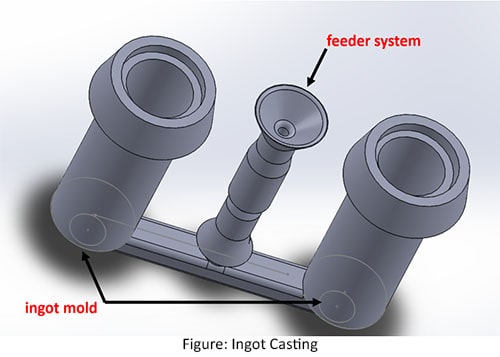
Ingot casting
There are two types of ingot casting methods. They are uphill teaming and vacuum casting.
In the Uphill teaming, molten steel is proved down through a vertical pipe called as feeder system which is then transferred to one or more horizontal pipes called as ingot mold who refer the melt further and drops it into the bottom of the vertical molds.
In the vacuum casting mold is placed in a vacuum tank and an intermediate ladle is position on top. The ladle on the vacuum tank is filled with molten steel. Then molten is pumped down in to casting mold. After fill the mold leave it to cool. Ingot casting is most commonly use to produce small batches of steel.
The steel thus formed is removed as a contaminate after use. Let us now consider the re-production of steel using steel scrap.
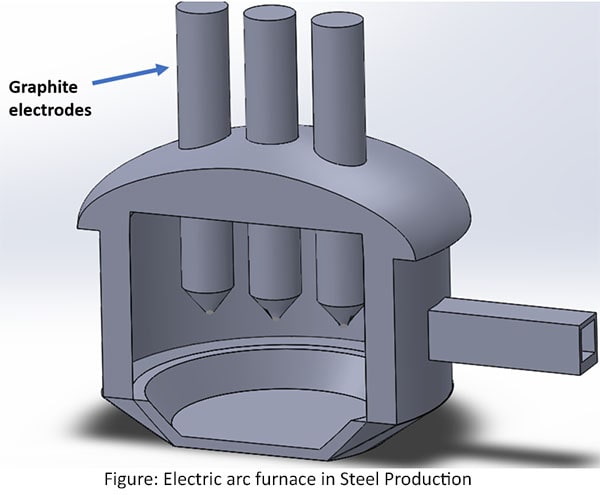
Electric arc furnace
Steel scrap is put into the furnace. Then electrodes are lowered in to the furnace. After, the powerful electric arc is given to increase temperature of the furnace about 120000C. Once the first load of steel scrap is melted further loads of scrap are added. To remove the impurities of steel, oxygen blown from the bottom of the liquid steel. The removing impurities are forming a slag. The slag rests on the steel, protecting it from contact with air.
The resulting liquid steel leads to a secondary steelmaking process mentioned above.
