Drawbacks and Risks of Operating a Bio Medical Incinerator without Flue Gas Treatment System
Biomedical waste is defined as the world's second hazardous waste category by the WHO and needs advanced disposal technology to properly dispose of this waste category. According to the WHO, Bio-Medical waste includes all the waste generated from the Health Care Facility that can have any adverse effect on the health of a person or to the environment in general if not disposed of properly.
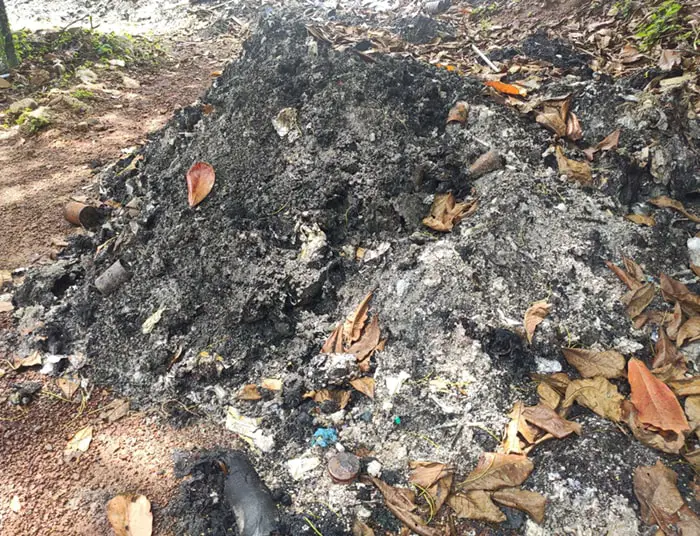

Photo: High quantities of Bottom Ash generation due to incomplete combustion of medical waste incineration in a hospital
Content
- Healthcare waste categories
- Solutions for Bio Medical Waste
- Flue gas generation in incineration process
- Components of flue gas generated by a Bio Medical Incinerator
- Line up a flue gas treatment system after combustion chambers
- Incinerators in Hospitals
- Small scale incinerators without flue gas treatment systems
- Emissions due to lack of flue gas treatment system
- Article by: Eng. Heshan Nipuna Demuni
Healthcare waste includes the following waste categories
- Human Anatomical Waste
- Animal Anatomical Waste
- Soiled Waste (such as Contaminated plastics and polythene with blood, and urine)
- Discarded or Expired Medicine
- Chemical Waste
- Chemical Liquid Waste
- Discarded linen, mattresses, and bedding contaminated with blood or body fluid, routine mask & gown.
- Microbiology, Biotechnology, and other clinical laboratory waste (Pre-treated)
- Waste Sharps including metals
Solutions for Bio Medical Waste
There are incineration and non-incineration solutions for disposing of healthcare waste and both methods are used with the preference of end users.
Flue gas generation in incineration process
In the case of using an incineration system, flue gas is generated which contains mainly Carbon dioxide, acidic gases, and also Dioxin and Furans as a result of the combustion process.
Components of flue gas generated by a Bio Medical Incinerator
- Carbon dioxide (CO2)
- Carbon monoxide (CO) - Highly toxic gas
- Water vapor (H2O)
- Sulfur dioxide (SO2) - An Acidic gas
- Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) - An Acidic gas
- Hydrogen chloride (HCl) - An Acidic gas
- Dioxin and Furan - these are persistent substances which have high resistance to degradation and can bioaccumulate in the food chain
- Dust particles
- Excess air (Oxygen and air)
Those highlighted in red colour are the most threatening gases and a detailed flue gas treatment system is compulsory to treat these acidic gases, dioxin and furans.
Line up a flue gas treatment system after combustion chambers
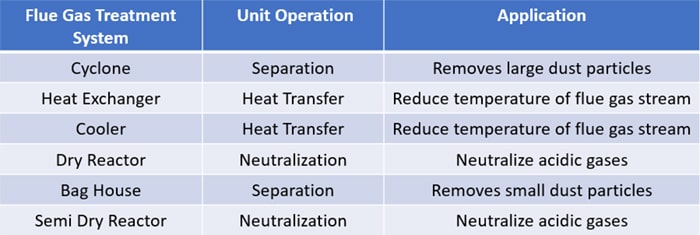
Therefore, it's compulsory to line up a systematic flue gas treatment system after the combustion process to minimize the emission of these toxic and hazardous gases in the flue gas stream. Flue gas treatment systems include the following unit operations.
- Second combustion chamber - Ensure complete combustion of all combustible materials and destroy Dioxin and Furans
- Cyclone system - Removes large-size dust particles
- Heat Exchanger - Significantly reduce the temperature of the flue gas stream
- Dry Reactor - Neutralize acidic gases
- Bag House / Bag Filters - Trap small-scale dust particles
- Semi-Dry Reactor - Furthermore neutralizes any remaining acidic gases
Incinerators in Hospitals
Incinerators are mostly installed in hospitals to dispose of Bio-Medical Waste as a solution within hospital premises.
Small scale incinerators without flue gas treatment systems
Unfortunately, most of the small-scale incinerators (such as 50kg/h) do not completely include or hardly use these flue gas treatment systems due to high capital investment and operational cost factors, specially in developing countries.
Emissions due to lack of flue gas treatment system
However, the outcomes of these poorly operated low-cost incinerators release extremely toxic and hazardous gaseous emissions into the ambient atmosphere. It causes many health risks to nearby humans and also harms the environment and animals.
Have Questions?