Preparation of Alkyl halides from Alcohols, Alkenes
There are methodologies to prepare Alkyl halide compounds under specific conditions. Same principles and methodologies can be used to synthesis every alkyl halide compound. In this tutorial, we will study how to prepare alkyl halides with examples.
Content
- Preparation of alkyl halides by the reaction of alcohols and Hydrogen acids
- General equation of alcohol and Hydrogen acids
- Ethanol and Hydrogen bromide reaction
- Mechanism of reaction of alcohols and Hydrogen acids
- Preparation of alkyl halides by the reaction of alkene and hydrogen acids
- General equation of alkene and Hydrogen acids
- Ethene and Hydrogen bromide reaction
- Mechanism of reaction of alkenes and Hydrogen acids
- Preparation of alkyl halides by the reaction of alcohols and inorganic acid chlorides
- General equations of alcohol and inorganic acid chlorides
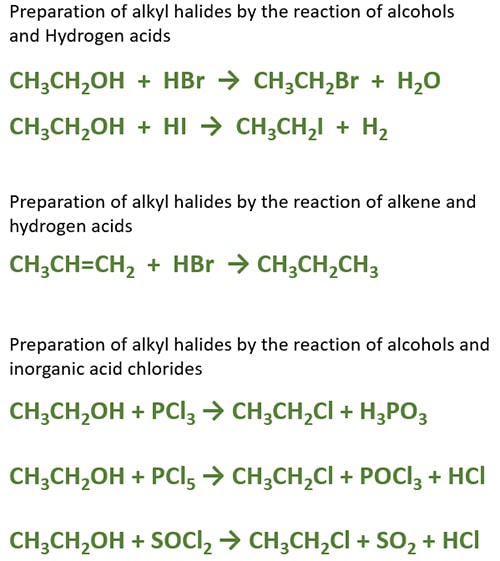
Preparation of alkyl halides by the reaction of alcohols and Hydrogen acids
Alkyl halide can be prepared by the reaction of halogen acids with alcohols. Hydrochloric (HCl), hydrobromic acid (HBr), Hydrogen iodide acid (HI) are halogen acids. Alcohols react with these acids and give alkyl halides. In this reaction , a halogen is substituted instead of hydroxyl group. As products, a major and minor product are given depending on the structure of alcohol.
General equation of alcohol and Hydrogen acids
ROH + HX → RX + H2O
NOTE: To occur the reaction easily with HCl, a catalyst ZnCl2 should be used.
Ethanol and Hydrogen bromide reaction
Bromoethane (ethyl bromide) will be given as the major-product while water is formed too.
CH3CH2OH + HBr → CH3CH2Br + H2O
Reaction rate of alcohols with HX
Reaction rate of alcohols and HX depends on the structure of alcohol type; primary or secondary or tertiary. Primary alcohols shows higher reaction rate than primary and secondary alcohol types for same number of carbon atoms. Reaction rate variation can be explained by the mechanism and the intermediate products of the reaction.

Mechanism of reaction of alkenes and Hydrogen acids
It's better to explain the mechanism from an example.
Propene and HBr reaction mechanism
There are two steps in this reaction mechanism.
- Formation of carbocation as an intermediate product
- Addition of bromine atom to the carbocation
In following figure, how 2-bromoprpopane is given as the major product.
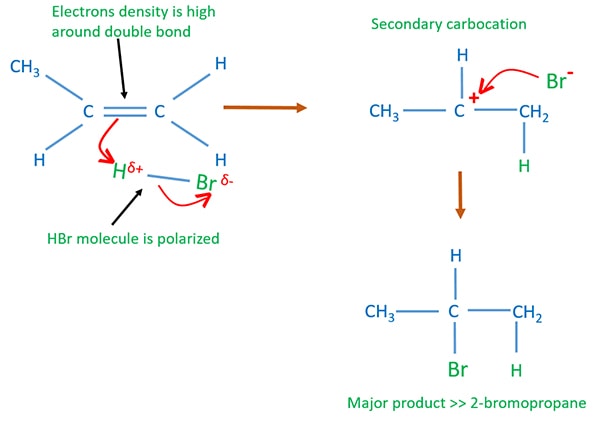
Preparation of alkyl halides by the reaction of alkene and hydrogen acids
Because alkenes are unsaturated aliphatic organic compound, addition reactions are possible. In alkene and hydrogen acid reaction, hydrogen and halogen atom of hydrogen acid is added to the carbon atoms in the double bond.
General equation for reaction of alkene and hydrogen acids
R1-C=CH2 + HX → R1-CX-CH3
Hydrogen atom of HX molecule is attached to the carbon atom (in the double bond) which has more hydrogen atoms. Halogen atom of HX molecule is attached to the other carbon atom.
Preparing alkyl halides by alcohols with inorganic acid chlorides
Alkyl chlorides are formed by the reaction of alcohols and inorganic acid chlorides. Phosphorus(III) chloride (PCl3) or Phosphorus(V) chloride (PCl5) or thionyl chloride (SOCl2) are used as inorganic acid chlorides. General equations of these reactions are mentioned below.
Alcohol and PCl3 reaction
ROH + PCl3 → RCl + H3PO3
Alcohol and PCl3 reaction
ROH + PCl5 → RCl + POCl3 + HCl
Alcohol and PCl3 reaction
ROH + SOCl2 → RCl + SO2 + HCl
Questions