Potassium permanganate and Sulfur dioxide Reaction | KMnO4 + SO2
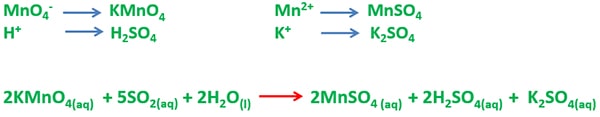
Potassium permanganate (KMnO4) reacts with sulfur dioxide (SO2) and give manganese sulfate, sulfuric acid and potassium sulfate. Manganese atom in KMnO4 is reduced and sulfur atom in SO2 is oxidized. Purple colour of aqueous KMnO4 solution is reduced to colourless or pale pink colour during the reaction.
Written by: Heshan Nipuna, Eng., Chemical & Process Engineering, University of Peradeniya, last modified: 26/09/2021
Balanced reaction of potassium permanganate and sulfur dioxide reaction is given below.
2KMnO4(aq) + 5SO2(g) + 2H2O(l) → 2MnSO4(aq) + 2H2SO4(aq) + K2SO4(aq)

Manganese in potassium permanganate is reduced from +7 oxidation state to +2 oxidation state (Mn2+). As well, sulfur in sulfur dioxide is oxidized from +4 oxidation state to +6 oxidation state (SO42-).
Because oxidation numbers of several elements in reactants are changed when products are given, this reaction is considered as a redox reaction.
Reaction medium should be slightly acidified by adding few drops of sulfuric acid.
Physical observations during the reaction of potassium permanganate and sulfur dioxide
Dilute aqueous potassium permanganate solution is a purple colour solution. When colourless sulfur dioxide gas is sent to that solution, purple colour of aqueous solution is decreased and become colourless or pale pink colour solution due to formation of Mn2+ cations.
Safety during the reaction
Sulfur dioxide is a toxic gas and acidic gas. Therefore, be careful to prevent any leakages during the treating sulfur dioxide gas in to the potassium permanganate solution.
How to balance KMnO4 and SO2 reaction
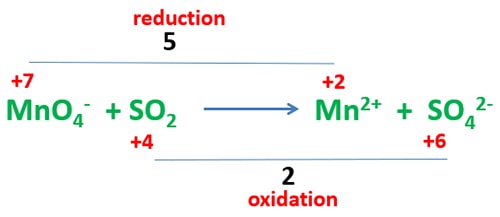
Identify oxidation number difference of elements
Because oxidation number of sulfur and manganese atoms are changed, identify what is the difference of oxidation numbers relevant to oxidation and reduction as below.
Exchange difference of oxidation numbers
Oxidation number difference of manganese atom is 5 and sulfur atom is 2. Then, exchange oxidation number difference as bellow.

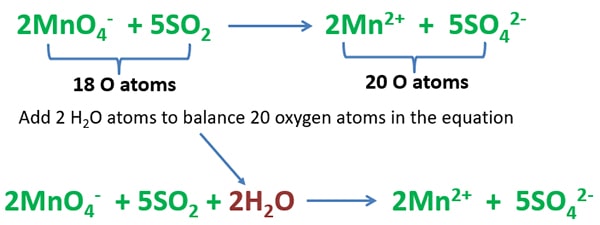
Balancing oxygen atoms
Count the total number of oxygen atoms in the left side and right side separately. To balance number oxygen atoms, add 2 H2O molecules to the left.
Balancing hydrogen atoms
Count the total number of hydrogen atoms in the left side and right side separately. To balance number hydrogen atoms, add 4 H+ ions to the right side.
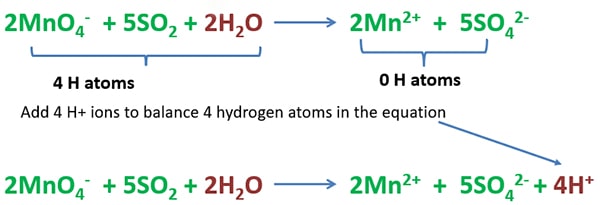
Now, we have obtained the balanced ionic equation.
Balancing chemical equation
Now, we need to balance the ionic equation.