Ammonia gas and Water Reaction in an Aqueous Solution | NH3 + H2O
Aqueous ammonia solution is a weak basic solution because ammonia molecules partially dissociates in water to produce ammonium cations and hydroxyl anions. Due to formation of hydroxyl ions, solution becomes a basic (alkaline) one. This reaction is a reversible reaction and pH value of the aqueous solution mainly depends on the concentration of the ammonia in the water.
In this tutorial, we will discuss followings.
- Solubility of ammonia gas in water
- Dissolving of ammonia gas in water:
- Reaction of ammonia with water
- Chemically balanced equation
- Dissociation of ammonia gas in water
- Change of oxidation numbers
- Physical and chemical observation when NH3 gas is dissolved in water
- Colour changes
- Odor of aqueous ammonia gas solution
- pH change of solution
- Safety, health hazards and environmental impacts possible due to this reaction
We can write several equations to describe how aqueous ammonia solution becomes basic in the water as below and will discuss in detail in this tutorial. Knowledge of physical chemistry is somewhat required to understand all the aspects of this reaction.
Solubility of ammonia in water
Ammonia is soluble in water and we can write a reversible reaction as below. In a closed system, aqueous ammonia solution comes to the equilibrium state between aqueous phase and gaseous phase. If system is a open one, system is not in an equilibrium state and dissolved ammonia gas will come to the gas phase from aqueous phase. In such case, ammonia concentration in water will be reduced with time.
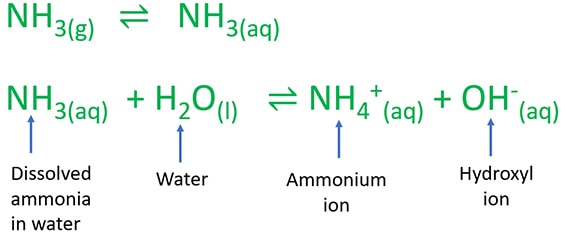
Dissolving of ammonia gas in water: NH3(g) ⇌ NH3(aq)
Above reaction represent, gaseous ammonia dissolve in water to give an aqueous solution. Addition to that, ammonia is readily soluble in water because ammonia molecules can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
Reaction of ammonia with water
Dissolved ammonia molecules reacts with water molecules to produce ammonium cations (NH4+) and hydroxyl ions. Because ammonium cation is unstable at water, it again reacts with water to produce ammonia gas.
NH3(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq)
Due to formation of hydroxyl ions in the aqueous medium, solution become basic and pH value increases more than 7. But, this dissociation is not strong like strong bases such as NaOH, KOH, etc.
Change of oxidation numbers
Ammonia and water reaction is not a redox reaction because oxidation numbers of atoms are not changed during the reaction process.
- In both ammonia molecule and ammonium chloride, nitrogen atom is at -3 oxidation state.
- Also, oxidation numbers of Hydrogen and Oxygen atoms are not changed during the reaction.
Physical and chemical observation when NH3 gas is dissolved in water
Here, we will see some physical observations and chemical properties changes during the reaction.
Colour changes
- There is no change in colour (colourless) when NH3 gas is dissolved and reacted with water.
- Therefore, you are unable to identify pure water and aqueous ammonia solution by only comparing colours.
Odor of aqueous ammonia gas solution
- There is a characteristic unpleasant odor in aqueous ammonia gas solution due to release of ammonia gas. But, never try to inhale this odor because ammonia gas is highly toxic and has the capability of causing severe injuries.
pH change of solution
Because aqueous ammonia solution contains more OH- ions than H3O+ ions, that solution should be basic. So, pH value is higher than 7. However basic characteristics aqueous ammonia solution is not strong as strong bases.
Safety, health hazards and environmental impacts possible due to ammonia solution
- Though ammonia solution is soluble in water, ammonia gas can be released to the atmosphere if ammonia solution container is not sealed or closed.
- Ammonia is a highly toxic gas to humans and avoid exposure of this solution. Ammonia is a colourless gas, but there is a very distinct odor and never to get exposed it.
Questions and Answers
How do I handle ammonia solution carefully in the laboratory?
Handling of ammonia solution can be classified to three sections.
- Storage: Make sure container is properly sealable to avoid gases emmision to outside. And also, properly sealing is important to avoid liquid overflows in an any accident such as fallings.
- Usage: Use an active fumehood when aqueous ammonia solution is fed to another container for an application. Fumehood will suck ammonia gas through the stack.