Chlorination of alkanes (methane) and mechanism
Chlorination of alkane gives a mixture of different products. When consider mechanism of alkanes chlorination, free radicals are formed during the reaction to keep the continuous reaction. Different alkyl chloride compounds, extended carbon chains compounds and HCl are formed as products in product mixture.
In this tutorial, we consider methane as the alkane compound and study about it's chlorination reactions steps, products and the mechanism. Also we disucss free radicals and their stability in mechanism of alkane and chlorine reaction which is important to decide major product and minor products.
For Alkane and Cl2 reaction, energy is required to occur the reaction.
Heat sources to occur the reaction
- Sunlight
- Ultra violet rays
- Energy produced from burning a magnesium metal
Methane chlorination | CH4 + Cl2
Methane does not react with Cl2 in dark. But when sun light exists, a mixture of chlorinated alkanes is given as products .
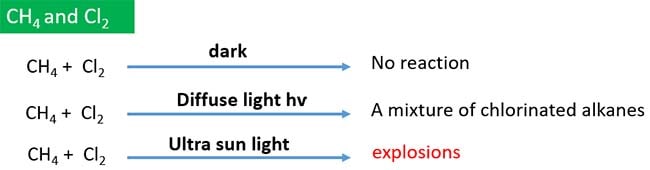
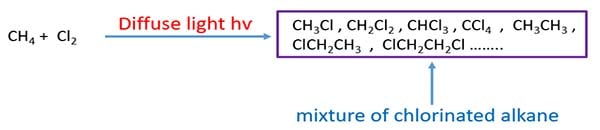
Products of methane chlorination
A mixture of chlorinated alkane is given as products after chlorination of methane. Otherwise we can say chlorination of methane gives differeent alkyl chlorides.
- Alkyl chlorides: CH3Cl, CH2Cl2, CHCl3, CCl4
- Hydrocarbons: CH3CH3, remaining CH4
- HCl
Mechanism of chlorine and methane reaction | reaction steps
Mechanism of chlorination of methane has three main steps. These all three steps are common for all alkanes chlorination mechanisms.
- Start of chains
- Propagation of chains
- End of chains
Start of chains in chlorination of alkanes
Cl2 molecules be subject to equal dissociation fragmentation and give Cl free radicals. These Cl free radicals are very reactive and unstable.
Propagation of chains
New free radicals are generated by reaction of existing free radicals and neutral molecules. Produced new free radicals carry the reaction forward furthermore. These steps and formation of new products are described in below sections.
Reaction steps
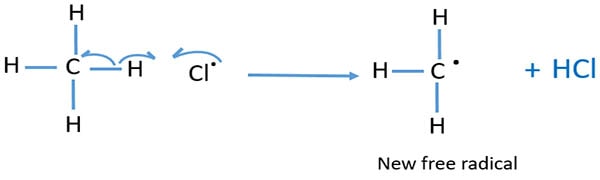
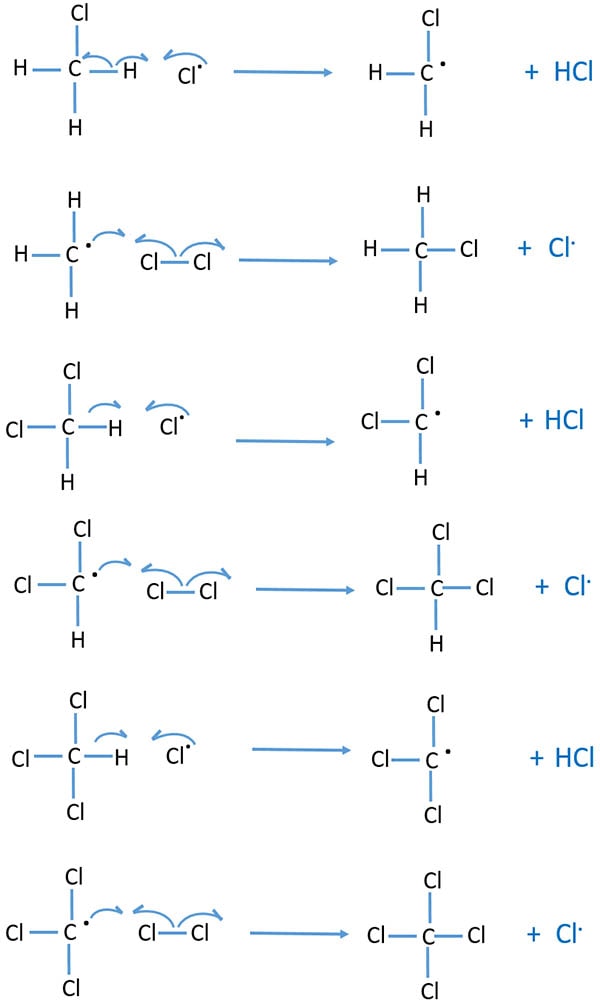
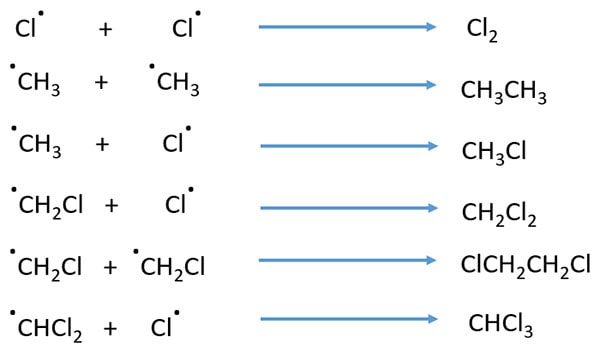
At the start, produced chlorine radical will break a C-H bond of CH4 and make HCl molecule and .CH3 radical. These .CH3 radical and chlorine radical react to form CH3Cl molecule.
Formed radicals can form more radicals. Formed .CH3 attack Cl2 molecule and it equally dissociate two chlorine radicals. One chlorine radical combine with .CH3 radical to give CH3Cl.
Existing CH3Cl molecule is attacked by chlorine radical to form .CH2Cl radical and HCl molecule. Formed .CH2Cl radical and .Cl combine together to produce CH2Cl2.
Two .CH3 radicals combine together to give CH3CH3.
End of chains in chlorination of alkanes
Two free radicals join and make a neutral molecule. Some example reactions are mentioned below.
- Two .CH3 radicals combine together to give CH3CH3 molecule.
- Two .Cl radicals form Cl2 molecule.
- .CH3 radical combines with .Cl radical to form CH3Cl molecule.
Obtain methylchloride as the product
By changing the methane and chlorine and ratio, methylchloride can be obtained as the product. Afterthat, by distillation the product mixture, methylchloride can be removed.
Free radicals
Free radicals are categorized as follow.
- Primary free radicals
- Secondry free radicals
- Tertiary free radicals
Stability of free radicals
Tertiary free radicals are the most stable free radicals while primary free radicals are the least.
Methylbenzene chlorination (Toluene)
There are hydrogen atoms in methyl group (-CH3) and phenyl group (-C6H5). But in the chlorination, chlorine atoms substitute hydrogen atoms in the methyl group.
Questions
What are the products given by chlorination reaction?
As organic compounds, Chloromethane, dichloromethane, trichloromethane, Carbon tetrachloride, ethane, etc. can be given as products.
Can propane be given as the product of chlorination of methane?
Yes. It is possible. In the chlorination mechanism, CH3 and CH2CH3 free radicals combine together as the end of chain reaction to give propane.
Propane: CH3CH2CH3