Ethene and Oxygen Reaction (Combustion) | CH2CH2 + O2
Ethene (Ethylene), an alkene compound in organic chemistry, readily burns with oxygen gas and heat is released as a result of combustion process. As chemical products, carbon dioxide and water are given if complete combustion of ethylene is achieved. Otherwise, some amount of carbon monoxide can be given as another product if the supplied oxygen gas amount is not sufficient for a complete combustion.
CH2CH2 + O2 → CO2 + H2O
In this tutorial, we will discuss followings.
Dimethyl ether (C2H4)
Ethene is a gas at room temperature due to its low molecular mass and weak secondary forces. It is highly flammable organic compound. There is a double bond between carbon atoms in ethene molecule.
Stoichiometric balanced chemical reaction of ethene and oxygen gases
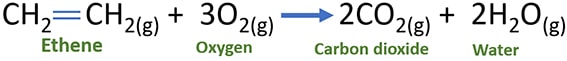
One mol of ethene react with three moles of oxygen gas and produce two moles of carbon dioxide and two moles of water.
CH2CH2(g) + 3O2(g) → 2CO2(g) + 2H2O(g)
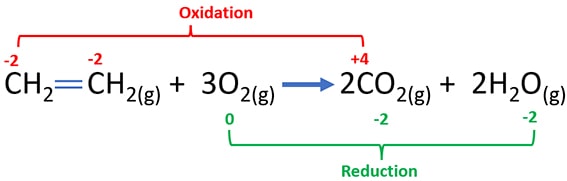
Change of oxidation numbers in propanol combustion
Because, above mentioned combustion process is a redox reaction (oxidizing and reducing), oxidation numbers of carbon and oxygen atoms are changed during the reaction as below.
- In C2H4 molecule, there are two carbon atoms exist and they are at same oxidation state (-2) as following figure. However, both carbon atoms are oxidized to carbon dioxide molecules due to combustion. In a carbon dioxide molecule, carbon is at +4 oxidation state. So, carbon atom is oxidized during the combustion process.
- Oxygen is at 0 oxidation state in oxygen molecule (O2) and that those oxygen atoms are reduced to -2 oxidation state as usual in combustion reactions. Therefore, oxygen atoms in oxygen molecule are reduced during the combustion process.
Thermal energy and heat generation of ethene
Standard enthalpy of combustion of ethene (ΔHc0(C2H4,(g))) = -1411.1 kJ mol-1
Health and safety
Ethene is a highly flammable chemical.
Questions
Both ethanol and methyl ether has same molecular formula, but have different structures. From ethanol and methyl ether, who has the higher combustion enthalpy?
Methyl ether's combustion enthalpy is higher than ethanol and combustion enthalpies of each chemical is mentioned below. So, you should understand that though chemicals with same chemical formula, but with different structures have different combustion enthalpies.
- Methyl ether: -1454.3584 kJ mol-1
- Ethanol: -1367.3584 kJ mol-1