Formaldehyde (CH2O) and Oxygen Reaction (Combustion) | HCHO + O2
Formaldehyde, the simplest aldehyde compound in organic chemistry, readily burns with oxygen gas and heat is released as a result of combustion. As chemical products, carbon dioxide and water are given if complete combustion of formaldehyde is achieved. Otherwise, some amount of carbon monoxide can be given as another product if supplied oxygen gas amount is not sufficient for a complete combustion.
HCHO + O2 → CO2 + H2O
In this tutorial, we will discuss followings.
Formaldehyde
- An aldehyde contains only one carbon atom, two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
- Pure formaldehyde exists as a gas at room temperature and aqueous solutions can be found in the market.
- It has founded that formaldehyde can be caused cancers.
Stoichiometric balanced chemical reaction of propanol and oxygen gases
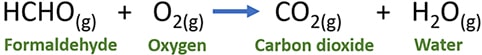
One mol of formaldehyde reacts with one mol of oxygen gas and produce one mol of carbon dioxide and one mol of water.
HCHO(l) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + H2O(g)
Change of oxidation numbers in propanol combustion
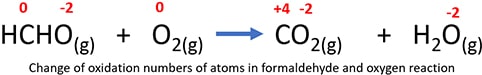
Because, above mentioned combustion process is a redox reaction, oxidation numbers of carbon and oxygen atoms are changed during the reaction as below.
- In formaldehyde molecule, carbon atoms exist at 0 oxidation state and that carbon atom is oxidized to carbon dioxide molecule. In a carbon dioxide molecule, carbon is at +4 oxidation state. So, carbon atom is oxidized.
- Oxygen is at 0 oxidation state in oxygen molecule (O2) and that those oxygen atoms are reduced to -2 oxidation state. Therefore, oxygen in oxygen molecule is reduced during the combustion process.
Thermal energy and heat generation
Standard enthalpy of combustion of formaldehyde (ΔHc0(HCHO,(l))) = -570.7 kJ mol-1
Health and safety
GHS hazard statements of formaldehyde and possible incidents are mentioned below.
- H301(83.33%): Toxic if swallowed [Danger Acute toxicity, oral]: Aqueous formalin solution contains formaldehyde and methanol. Proper labeling is compulsory in handling.
- H311 (83.33%): Toxic in contact with skin [Danger Acute toxicity, dermal]: Always wear full overall during handling time period.
- H314 (83.33%): Causes severe skin burns and eye damage [Danger Skin corrosion/irritation]: Wear safety goggles to protect eyes.
- H317 (91.5%): May cause an allergic skin reaction [Warning Sensitization, Skin]
- H318 (46.13%): Causes serious eye damage [Danger Serious eye damage/eye irritation]
- H330 (12.3%): Fatal if inhaled [Danger Acute toxicity, inhalation]: Use a fume hood to remove formaldehyde vapor and wear a respiratory protection devices.
- H331 (79.37%): Toxic if inhaled [Danger Acute toxicity, inhalation]
- H341 (19.08%): Suspected of causing genetic defects [Warning Germ cell mutagenicity]
- H350 (19.08%): May cause cancer [Danger Carcinogenicity]
- H351 (64.3%): Suspected of causing cancer [Warning Carcinogenicity]
Questions