Oxalic acid and sodium hydroxide reaction | H2C2O4 + NaOH
Oxalic acid (H2C2O4)is a dibasic weak acid and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is a strong base. When oxalic acid reacts with sodium hydroxide, sodium oxalate (Na2C4O4) and water (H2O) are given as products. As well, this reaction is an example to weak acid and strong base reaction.
H2C2O4(aq) + NaOH(aq) → Na2C4O4(aq) + H2O(l)
In this tutorial, we will discuss followings.
Stoichiometric balanced chemical reaction of H2C2O4 and NaOH
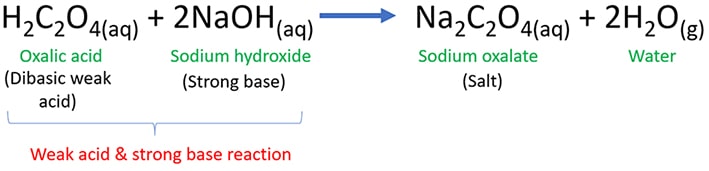
H2C2O4(aq) + 2NaOH(aq) → Na2C4O4(aq) + 2H2O(l)
According to the above balanced equation, 1 mol of oxalic acid reacts with 2 mol of sodium hydroxide and as products, 1 mol and 2 moles of sodium oxalate and water are given respectively.
Aqueous oxalic acid solution is colourless and aqueous sodium oxalate solution is colourless too.
Heat of neutralization reaction
Because, oxalic acid is a weak acid, it absorbs some heat to dissociate to H+ and C2O42- ions. As a result, net output heat of neutralization of oxalic acid with sodium hydroxide is less than (-57.1 *2 = -114.2) kJ.
Enthalpy change of neutralization of strong acid and strong base is taken as -57.1 kJ mol-1 (considering 1 mol of water generation)
Oxalic acid contains two hydrogen atoms which can be released as two H+ ions. Because two sodium hydroxide moles are required for the reaction, two hydroxyl ions reacts with two H+ ion moles as below mentioned equation. That's why net output heat should be less than -57.1 *2 kJ.
2H+ + 2OH- → 2H2O
Applications of reaction of oxalic acid and sodium hydroxide
- Sodium hydroxide is used to titrate non-adsorbed oxalic acid in the experiment of determining of adsorption isotherm of aqueous oxalic acid on activated charcoal conducted under chemistry practical series in universities.
Questions