Silver nitrate and Hydrochloric acid Reaction | AgNO3 + HCl
When aqueous silver nitrate (AgNO3) and aqueous Hydrochloric acid (HCl) are reacted, Silver chloride (AgCl) precipitate and nitric acid (HNO3) are given as chemical products. Silver chloride is a white precipitate and nitric acid exists as an aqueous solution.
However, according to the concentration or added amount of hydrochloric acid, there is a possibility to give a coordination complex ion, [AgCl2]-.
In this tutorial, we will discuss followings.
Dilute hydrochloric acid and silver nitrate aqueous solution
As explained earlier, Silver chloride(AgCl) and nitric acid are given as products. Because AgCl is a white precipitate, it is not soluble in water.
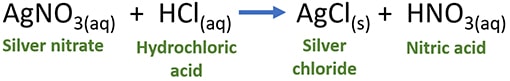
Stoichiometric balanced reaction of AgNO3 and HCl
AgNO3(aq) + HCl(aq) → AgCl(aq) + HNO3(aq)
According to the above balanced equation, one silver nitrate mol reacts with one hydrochloric acid moles and gives one mol of silver chloride and one mol of nitric acid.
With concentrated hydrochloric acid or excess hydrochloric acid
In the presence of excess chloride ion, AgCl precipitate is soluble. If concentrated hydrochloric acid or excess hydrochloric acid is added to aqueous silver nitrate solution or silver chloride precipitate, Dichoroargentate(1-) ion is given.
AgCl(s) + HCl(aq) → [AgCl2]-(aq) + H+
Change of oxidation numbers
This reaction is not a redox reaction because oxidation numbers of atoms are not changed during the reaction process.
- In both AgNO3 and AgCl, silver is at +1 oxidation state.
- Nitrogen's oxidation number in HNO3 and nitrate ion (NO3-) ion is +5.
Physical and chemical observation of AgNO3 and HCl reaction
Here, we will see some physical observations and chemical properties changes during the reaction. These observations are important to identify compounds from other compounds in the qualitative analysis.
Colour changes
- Both silver nitrate and hydrochloric acid are colourless aqueous solutions.
- You will see a white precipitate is formed because silver chloride is produced. But, other product nitric acid is a colourless aqueous solution.
pH change of solution
If hydrochloric acid is added to silver nitrate solution, because of nitric acid is given as a product, pH value of silver nitrate containing solution is increased.
Safety and health hazards possible due to this reaction
- Silver nitrate may intensify fire,Causes severe skin burns and eye damage and very toxic to aquatic life
- Also, hydrochloric acid is a dangerous and corrosive chemical, handle it carefully. Specially, if you use concentrated hydrochloric acid, wear a proper respirator, eye protection goggles and chemical resistant gloves to protect your respirator system, eyes and hands.
- Because nitric acid is formed as a product, again be careful when you dispose of the final solution.
Questions